How to operate a drone unveils the fascinating world of unmanned aerial vehicles. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the various types and their unique functionalities to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, basic and advanced maneuvers, and even delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial photography and videography.
Prepare to take flight!
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to learning how to safely and effectively pilot a drone. We cover everything from selecting the right drone for your needs to understanding and complying with relevant regulations, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience. Whether you are a complete beginner or looking to improve your existing skills, this guide offers valuable insights and practical advice.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the distinctions between multirotor, fixed-wing, and hybrid drones, along with a comparison of their control interfaces and examples of specific models.
Multirotor, Fixed-Wing, and Hybrid Drone Operation
Multirotor drones, characterized by their multiple rotors, offer exceptional maneuverability and the ability to hover. They are ideal for close-range photography and inspection tasks. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, are faster and have a longer range, making them suitable for large-area mapping and surveying. Hybrid drones combine features of both, providing versatility for various applications. Operational differences stem primarily from their flight characteristics: multirotors are highly agile but have shorter flight times, while fixed-wing drones require runways for takeoff and landing but offer greater endurance.
Drone Control Interfaces
Control interfaces vary significantly across drone models. Many utilize handheld radio controllers, providing intuitive control over throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw. More advanced models incorporate smartphone or tablet apps for enhanced control and features like GPS waypoint navigation and autonomous flight modes. Some professional drones even use specialized ground control stations with larger displays and more sophisticated control options.
Examples of Drone Models and Unique Operational Features
The DJI Mavic 3 boasts impressive camera capabilities and obstacle avoidance, while the Autel EVO II offers interchangeable camera modules for diverse applications. Fixed-wing drones like the SenseFly eBee X are known for their efficient mapping capabilities. Hybrid drones are less prevalent but are increasingly being developed to cater to specific needs.
Drone Type Comparison Table
| Drone Type | Flight Time | Range | Payload | Control Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 (Multirotor) | 46 minutes (approx.) | 15 km (approx.) | 500g (approx.) | GPS, Obstacle Avoidance, Intelligent Flight Modes |
| Autel EVO II (Multirotor) | 40 minutes (approx.) | 9 km (approx.) | 1 kg (approx.) | GPS, Obstacle Avoidance, Return-to-Home |
| SenseFly eBee X (Fixed-Wing) | 50 minutes (approx.) | 15 km (approx.) | 200g (approx.) | Autonomous Flight Planning, Precision Mapping |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves verifying battery levels, inspecting the drone for any damage, and checking for environmental factors that might affect flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include:
- Battery level check and charging
- Visual inspection of propellers, motors, and airframe for damage
- GPS signal acquisition and satellite count verification
- Checking local weather conditions and airspace restrictions
- Confirmation of controller connection and calibration
- Review of flight plan and intended area of operation
Battery Checks and Charging Procedures
Always ensure your drone’s batteries are fully charged and in good condition. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper charging procedures to avoid damage or safety hazards. Using damaged or improperly charged batteries can lead to malfunctions or even catastrophic failures during flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation (text-based) of a pre-flight inspection flowchart:
- Inspect drone for physical damage
- Check propeller tightness
- Verify battery charge level
- Check GPS signal strength
- Review weather conditions
- Confirm airspace restrictions
- Calibrate the controller
- Power on drone and controller
Potential Pre-Flight Problems and Solutions
Here’s a list of potential pre-flight problems and their solutions:
- Low battery: Charge the battery fully.
- No GPS signal: Move to an open area with clear sky visibility.
- Controller malfunction: Check for battery issues or try recalibrating.
- Propeller damage: Replace damaged propellers.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective drone operation. This section details the functions of the primary controls and provides a step-by-step guide for performing basic maneuvers.
Primary Flight Controls
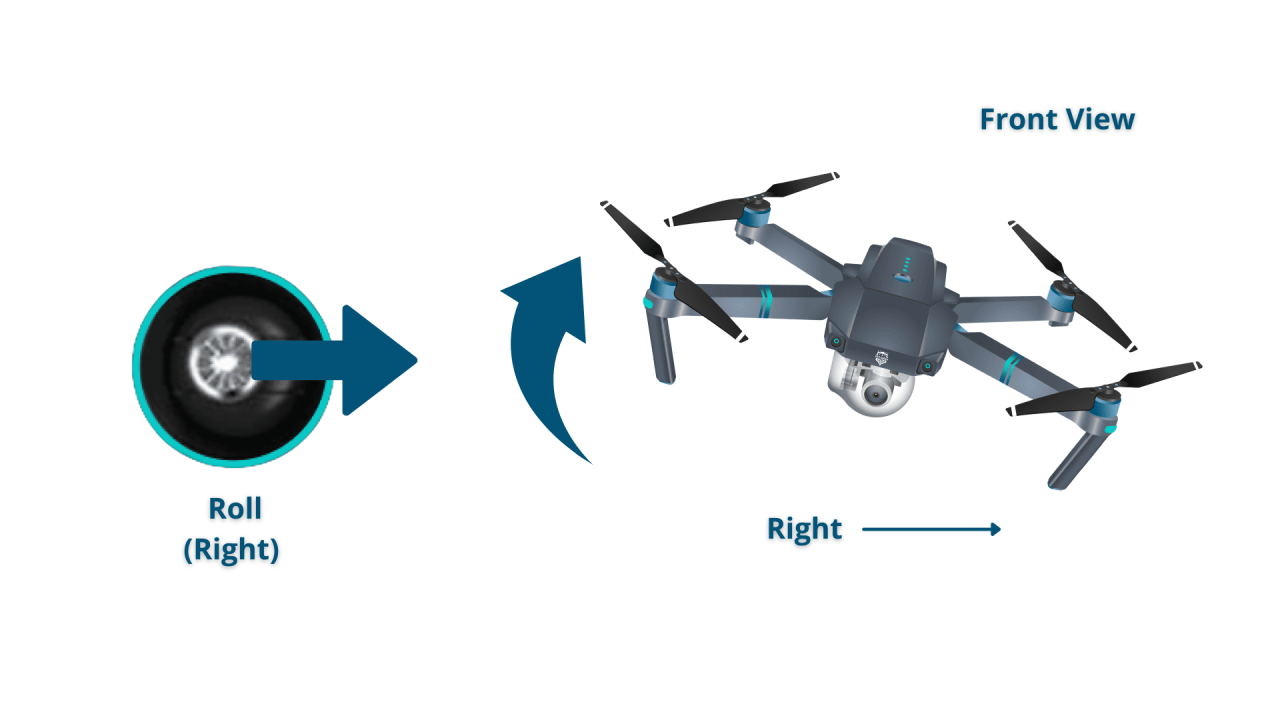
The primary flight controls are throttle (controls altitude), pitch (forward/backward movement), roll (left/right movement), and yaw (rotation). Understanding how these controls interact is essential for smooth and controlled flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a good understanding of regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which will greatly assist you in becoming a proficient drone pilot.
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount, so thorough preparation is essential before taking to the skies.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
Taking off involves gently increasing the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground. Hovering requires maintaining a steady throttle to keep the drone at a consistent altitude. Landing involves gradually decreasing the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include turning (using yaw control), ascending (increasing throttle), and descending (decreasing throttle). These maneuvers should be practiced in a controlled environment before attempting more complex maneuvers.
Example Flight Path
A simple maneuver might involve taking off, hovering for a few seconds, performing a 90-degree turn to the right, ascending to a higher altitude, descending back to the original altitude, and then landing. This involves coordinated use of throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw controls.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques require a higher level of skill and understanding of drone dynamics. This section explores flying in windy conditions, hazard identification, precise positioning, and different flight modes.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Windy conditions present significant challenges. Strategies for mitigation include flying on less windy days, choosing sheltered locations, and adjusting flight parameters to compensate for wind gusts. Experienced pilots might use wind-resistant flight modes or techniques to maintain stability.
Potential Hazards and Safety Protocols
Potential hazards include obstacles, low battery, loss of signal, and adverse weather conditions. Safety protocols include maintaining visual line of sight, avoiding crowded areas, and having a backup plan in case of malfunctions. Regularly checking battery levels and signal strength is crucial.
Precise Positioning and Stable Hovering
Precise positioning and stable hovering are essential for tasks like photography and inspection. This often requires using GPS-assisted flight modes and advanced features like waypoint navigation. Practicing in calm conditions helps develop the necessary skills.
Flight Modes

Different flight modes, such as GPS mode (relies on GPS for position and stability) and attitude mode (relies on onboard sensors), offer varying levels of control and stability. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each mode is important for adapting to different flying conditions.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. This section explores techniques for capturing high-quality footage, camera settings, and cinematic video planning.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Footage
Capturing high-quality aerial footage involves understanding camera settings, composition, and lighting. Smooth movements and careful planning are crucial for professional-looking results. Experimentation is key to mastering different styles and techniques.
Impact of Camera Settings
Aperture, shutter speed, and ISO significantly impact drone footage. A wider aperture (lower f-stop) allows more light, resulting in a shallower depth of field. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. ISO controls sensitivity to light, impacting image noise.
Cinematic Drone Video Plan
A short cinematic drone video might involve establishing shots of the landscape, followed by dynamic tracking shots of a subject, interspersed with close-up details. Varying camera angles and heights creates visual interest and depth.
Camera Angles and Shots
Common camera angles include high-angle shots (looking down), low-angle shots (looking up), and eye-level shots. Shots like pans, tilts, and orbits add dynamic movement and visual appeal.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Adhering to local and national drone regulations is crucial for safe and legal drone operation. This section details the importance of airspace restrictions and responsible drone operation practices.
Importance of Adhering to Drone Regulations

Drone regulations are in place to ensure safety and prevent accidents. Violating these regulations can lead to fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges. It’s essential to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before flying.
Airspace Restrictions
Airspace restrictions exist around airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. Checking for airspace restrictions before each flight is mandatory using online tools or apps provided by aviation authorities. Unauthorized flights in restricted airspace are illegal and dangerous.
Responsible Drone Operation Practices, How to operate a drone
Responsible drone operation includes maintaining visual line of sight, avoiding crowded areas, and respecting privacy. Flying responsibly protects the public and ensures the continued acceptance of drone technology.
Potential Legal Consequences
Potential legal consequences for violating drone regulations include fines, temporary or permanent license suspension, and even criminal charges depending on the severity of the violation. Understanding the legal framework is paramount.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. This section provides troubleshooting guides for common issues and basic drone maintenance procedures.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, motor failures, and controller connectivity issues. Causes can range from battery issues and environmental factors to mechanical problems or software glitches.
Troubleshooting Guides
Troubleshooting steps typically involve checking battery levels, restarting the drone and controller, checking for physical damage, and potentially contacting the manufacturer for support. Following manufacturer’s troubleshooting guides is recommended.
Basic Drone Maintenance
Basic maintenance includes regularly inspecting propellers, motors, and the airframe for damage. Cleaning the drone after each flight is also recommended. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Common Error Messages and Solutions
| Error Message | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge | Charge the battery fully. |
| GPS Signal Lost | Obstructed GPS signal | Move to an open area with clear sky visibility. |
| Motor Failure | Damaged motor or propeller | Inspect and replace damaged components. |
| Controller Disconnected | Low controller battery or interference | Check controller battery and try recalibrating. |
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible practice. From understanding the nuances of different drone types and their controls to navigating airspace regulations and capturing breathtaking aerial footage, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on your drone adventures safely and responsibly. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot.
Soar high, but always fly smart!
FAQ Insights: How To Operate A Drone
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functions, and intuitive control interfaces. Research reviews and compare features before making a purchase.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful planning and practice; learning the basics is crucial before taking flight. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from takeoff to landing, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone , which will help you become a confident and responsible drone pilot.
Safe and proficient drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and legal compliance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically bring the drone back to its takeoff point if signal is lost. However, it’s important to always maintain visual contact with your drone and be prepared to manually take control if possible.
How do I obtain the necessary permits for drone operation?
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority or government agency to determine any necessary permits or licenses before operating your drone. Failure to comply with regulations can result in fines or legal action.